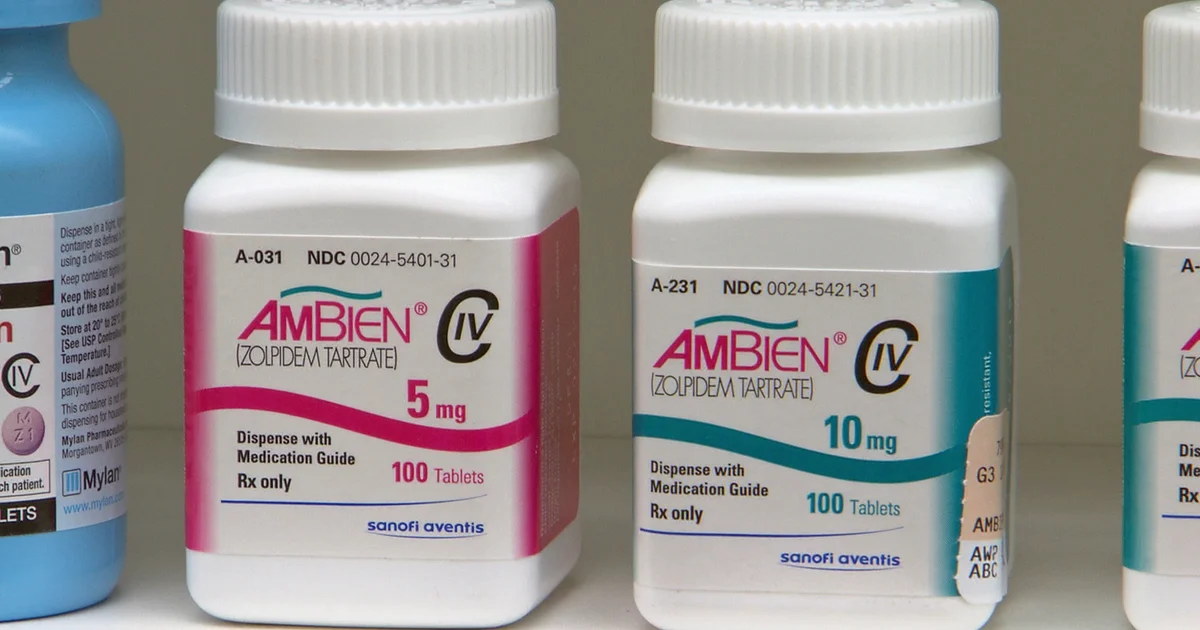
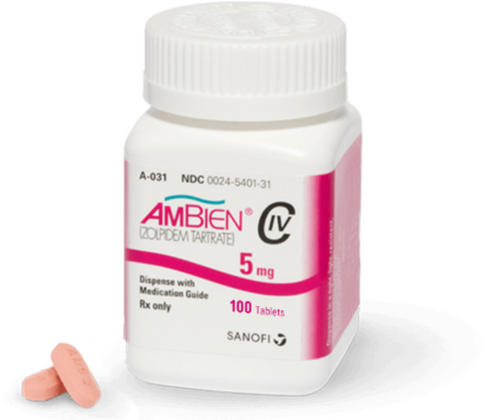
Ambien (zolpidem)
£100.00
Ambien (Zolpidem) – Prescription Sleep Aid for Insomnia Relief
Ambien (Zolpidem) is a trusted prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia and other sleep-related difficulties. It works by calming the brain and nervous system, helping you fall asleep faster and enjoy a full, restful night’s sleep.
Available Strengths and Packaging
Ambien is available in a range of dosages and packaging sizes, making it easy to find the right option for your needs:
-
5 mg tablets – typically recommended for beginners or individuals sensitive to medication.
-
10 mg tablets – standard dose for most adults.
-
Ambien CR (Controlled Release) – available in 6.25 mg and 12.5 mg, designed to help you fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Ambien is usually supplied in:
-
Bottles of 30, 60, or 90 tablets (depending on the pharmacy or distributor).
-
Blister packs for individual doses, ensuring freshness and safety.
Quality and Authenticity
All Ambien (Zolpidem) tablets are pharmacy-grade, FDA-approved, and manufactured under strict quality control standards to ensure purity, safety, and effectiveness. Each tablet is film-coated for easy swallowing and quick absorption, offering consistent potency and high reliability.
Quantity and Size
-
Tablet size: small, oval, or oblong (depending on manufacturer).
-
Color: may vary (commonly white or pink).
-
Available quantities: 30, 60, 90, or 120 tablets per bottle.
-
Each bottle is tamper-evident and clearly labeled with dosage and expiration details.
How to Use Ambien (Zolpidem)
-
Take Ambien exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
-
It is usually taken once nightly, just before bedtime.
-
Do not take Ambien unless you can get a full 7–8 hours of sleep before you need to be active again.
-
Take the tablet on an empty stomach for faster effect.
-
Do not crush, chew, or break the extended-release (Ambien CR) tablets — swallow them whole.
-
Avoid alcohol or other sedatives while using Ambien.
Important Usage Notes
-
Ambien is meant for short-term use (generally 1–2 weeks) unless otherwise directed by your doctor.
-
Misuse or long-term dependence can occur — always follow medical advice.
-
Store in a cool, dry place away from light and moisture.
Description
What is Ambien (zolpidem) and how does it work?
In short: Ambien (zolpidem) is a sedative-hypnotic medication used largely for short-term treatment of insomnia. It helps people fall asleep faster and, depending on formulation and dose, may also help maintain sleep. It acts by enhancing the activity of GABA_A receptors in the brain, which slows down neuronal excitation and induces sleep.Wikipedia+2PMC+2
Uses and Indications
-
Primary use: Treatment of insomnia disorder, especially when people have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.Wikipedia+2PMC+2
-
Formulations: Immediate-release (helps with sleep onset), extended-release (helps stay asleep), sublingual tablets, etc.Wikipedia+1
-
When to use: It should be used when non-drug approaches (sleep hygiene, behavioral therapy) have not been sufficient. It is usually prescribed for short durations, because risks increase with longer use.Wikipedia+1
Efficacy: What the Evidence Shows
Studies have repeatedly found that Ambien (zolpidem) can:
-
Reduce sleep latency (the time it takes to fall asleep). In trials, subjects on zolpidem show significantly shorter latency compared to placebo.PMC+2ScienceDirect+2
-
Increase total sleep time and decrease nighttime awakenings.ScienceDirect+2PMC+2
-
Modify sleep architecture: Zolpidem tends to increase non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, particularly slow-wave sleep (deep sleep), and reduce REM sleep in some doses.ScienceDirect+3Oxford Academic+3PMC+3
However, effects vary by dose, formulation, age, and individual metabolism. Some studies found minimal disturbance in sleep stages at lower doses.Oxford Academic+1
Risks, Side Effects, and Limitations
While Ambien (zolpidem) works for many, it comes with important risks and limitations:
-
Daytime drowsiness, impaired alertness: Even though its half-life is relatively short (~2-3 hours for many formulations), residual effects can persist, especially in women and older adults.Wikipedia+2PMC+2
-
Cognitive and memory effects: Some people experience memory impairment, especially related to sleepwalking, anterograde amnesia, or other parasomnias.ScienceDirect+3Wikipedia+3PMC+3
-
Tolerance, dependence, withdrawal: Regular use over longer periods may lead to reduced effectiveness, physical dependence, and difficulty stopping.ScienceDirect+1
-
Adverse sleep architecture changes at higher doses: Some studies show that high doses reduce REM sleep or alter deep sleep stages unfavorably.ScienceDirect+2PBM VA+2
Best Practices for Use
To maximize benefits and reduce risks:
-
Start with the lowest effective dose. Using higher than necessary dose increases side effect risks.
-
Use short-term only, ideally under medical supervision. Long-term use should be weighed carefully.
-
Avoid alcohol and other sedatives when using Ambien (zolpidem). These can amplify sedative effects and risk.
-
Ensure safety: Before waking, allow enough time (ideally 7-8 hours) so that residual sedation won’t impair daytime functioning.
-
Monitor for unusual behaviors: Sleepwalking, sleep driving, complex behaviors should prompt medical review.
Mechanism of Action
Ambien (zolpidem) works by selectively binding to GABA_A receptor sites (especially those containing the α1 subunit), enhancing the effect of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. This binding hyperpolarizes neurons in brain regions involved in promoting wakefulness, thereby facilitating sleep onset and maintenance.Wikipedia+2Nature+2
Regulatory & Safety Profile
-
The drug is approved in many countries under brand names such as Ambien; generic zolpidem is available.Wikipedia
-
It is a controlled substance in many jurisdictions due to risk of dependency and abuse potential.Wikipedia
-
Guidelines often recommend that cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia be tried before or alongside drug therapy.Wikipedia
Related Information & Further Reading
For more detailed pharmaceutical guidance, dosing, legal status, and prescribing norms, see The Pharmacy Meds (internal link).
To learn more about pharmacology, chemical structure, side effects and broader physiological data, see the Wikipedia article on zolpidem. For example: Zolpidem – Wikipedia. Wikipedia
Conclusion
Ambien (zolpidem) offers a validated option for people struggling with insomnia. It speeds sleep onset, can lengthen total sleep, and improves sleep quality for many individuals. But its benefits come with real risks—cognitive effects, dependency, altered sleep architecture, and residual sedation. To get the best results, use it for short periods, at low doses, with behavioral interventions, and under medical oversight.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.