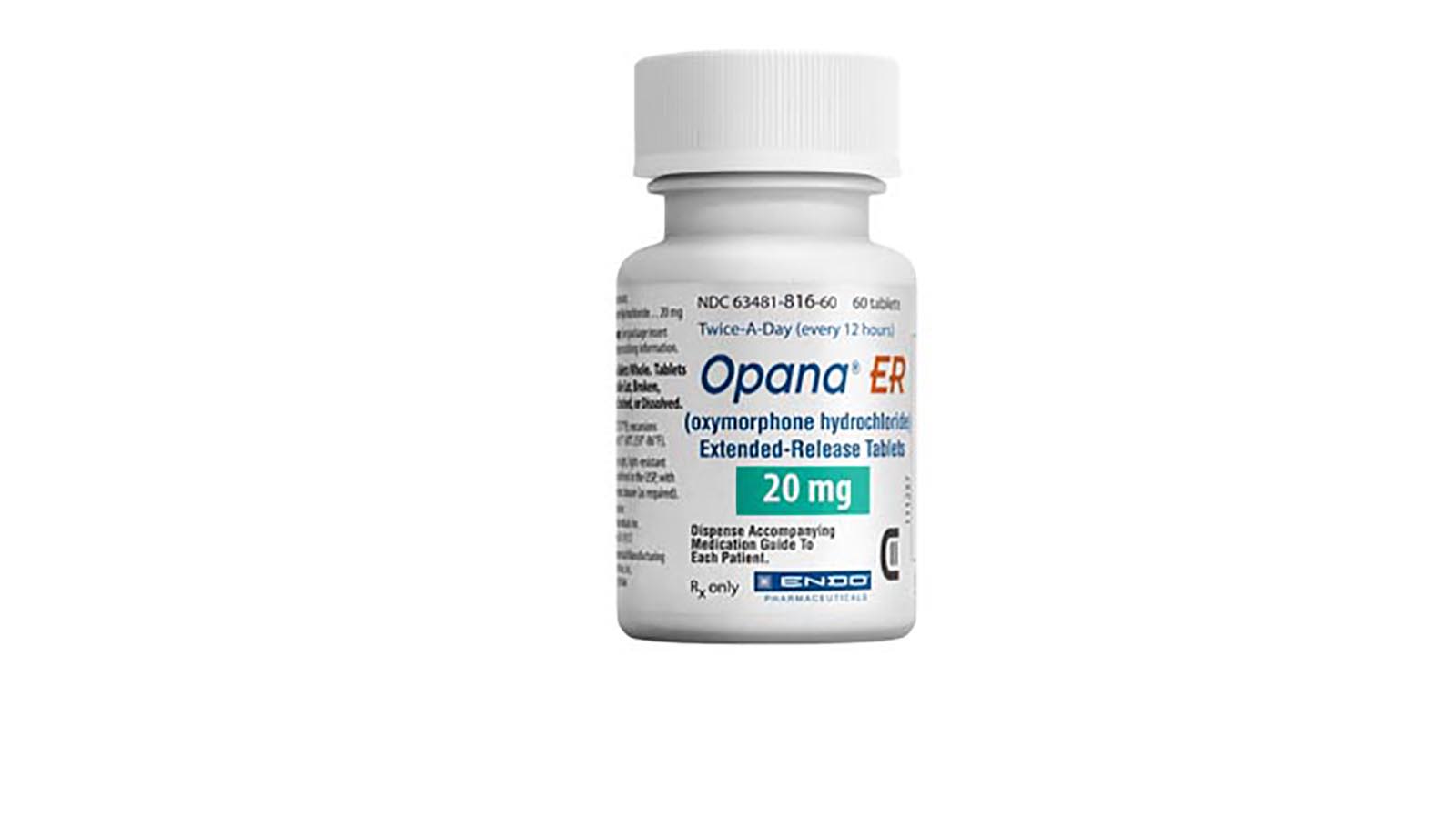
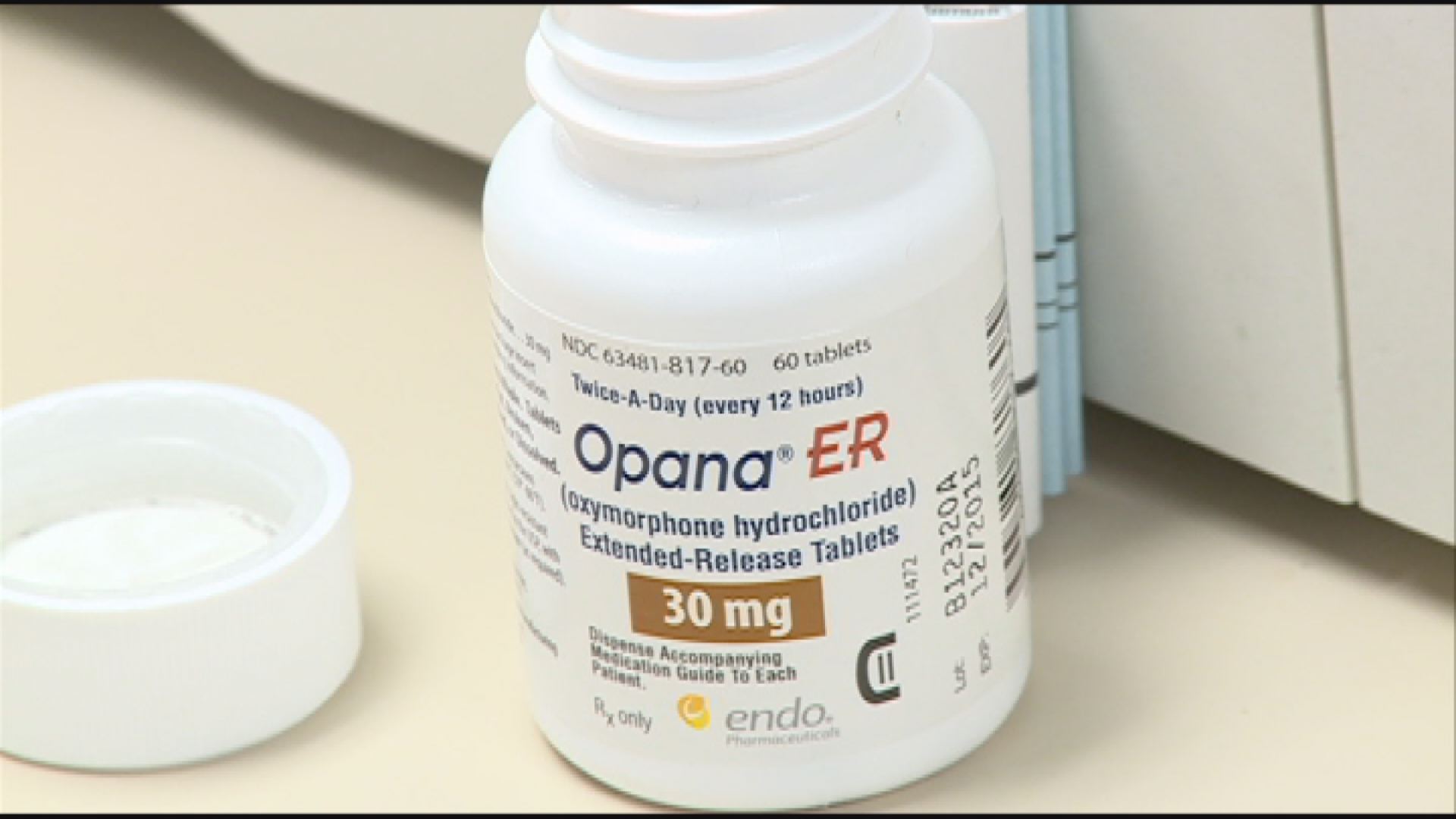
Opana ER
£28.00
Opana ER (Extended-Release Oxymorphone Hydrochloride)
Description:
Opana ER is a prescription opioid medication used for the management of moderate to severe pain when around-the-clock pain relief is needed. It contains oxymorphone hydrochloride, a potent opioid analgesic. Opana ER works by binding to specific receptors in the brain and spinal cord to reduce the perception of pain. This medication is designed for extended-release, providing long-lasting pain relief over 12 hours.
Available Strengths (MGs):
Opana ER is commonly available in the following dosages:
-
5 mg
-
10 mg
-
15 mg
-
20 mg
-
30 mg
-
40 mg
Packaging / Bottles:
Opana ER is typically supplied in bottles containing 30 tablets, although packaging may vary depending on the manufacturer and region. Always check the label for exact quantity and expiration date.
Quality:
-
Manufactured according to strict pharmaceutical standards to ensure purity, potency, and safety.
-
Each tablet is extended-release, meaning it is formulated to release the active ingredient gradually over time for consistent pain control.
Size / Form:
-
Round or oval tablets, coated for easier swallowing.
-
Designed to prevent crushing or chewing to avoid accidental overdose.
How to Use:
-
Take exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
-
Swallow tablets whole with water; do not crush, chew, or dissolve.
-
Can be taken with or without food, but try to be consistent with timing.
-
Dosing frequency is usually every 12 hours, depending on your doctor’s instructions.
-
Avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants while taking Opana ER, as they can increase the risk of serious side effects.
Important Notes:
-
This medication is highly addictive and should be used with caution.
-
Do not share with anyone, especially someone with a history of substance abuse.
-
Monitor for side effects such as dizziness, constipation, nausea, or slowed breathing, and contact your doctor if severe reactions occur.
Description
Opana ER is the trade name for extended-release oxymorphone hydrochloride, a prescription opioid intended to treat moderate to severe chronic pain when non-opioid therapies are inadequate. Its formulation releases oxymorphone over an extended period, allowing around-the-clock pain control rather than requiring frequent dosing. it was approved by the FDA in 2006. FDA Access Data+2Medscape Reference+2
Oxymorphone, the active ingredient in Opana ER, is a potent mu-opioid receptor agonist. It reduces perception of pain by binding to receptors in the brain and spinal cord. For more on oxymorphone generally (its pharmacology, addiction liability, and legal status), see the Wikipedia entry. Wikipedia
How Does Opana ER Work? Pharmacokinetics & Dose
-
After oral administration, Opana ER releases oxymorphone slowly to maintain stable blood levels over ~12 hours. FDA Access Data+2Medscape Reference+2
-
It has relatively low bioavailability by mouth (≈10 %) due to first-pass metabolism. Wikipedia+1
-
The drug metabolizes in the liver via CYP3A4 and glucuronidation; inactive and active metabolites form. Wikipedia+1
Indications: When Is Opana ER Used?
Opana ER is indicated for patients:
-
Who suffer from severe, ongoing pain requiring constant around-the-clock opioid therapy. Medscape Reference+1
-
When other options (non-opioid analgesics or immediate-release opioids) either do not work, cause intolerable side effects, or are impractical. Medscape Reference+1
Risks, Side Effects & Evidence of Harm
While Opana ER can relieve pain, it carries significant risks. Evidence from clinical studies, regulatory actions, and case reports shows serious adverse outcomes.
Common Side Effects
-
Nausea, vomiting, constipation, dizziness, dry mouth, somnolence. DrugBank+2Medscape Reference+2
-
Respiratory depression, especially when used with other central nervous system depressants (e.g. alcohol, benzodiazepines). Overdose risk rises sharply. Medscape Reference+1
Serious and Rare Risks
-
Abuse, Dependence & Withdrawal
Opana ER has a high potential for misuse. People may crush or dissolve the tablets to snort or inject them to achieve a faster high. That increases overdose risk. PMC+2Wikipedia+2
-
Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)
A documented case report describes a patient who developed TMA after years of injecting Opana ER. The FDA and Centers for Disease Control have linked certain outbreaks of TMA to intravenous misuse of Opana ER. PMC+1
-
Public Health Concerns & Market Withdrawal
Because of growing evidence that reformulated Opana ER still was being misused (injected), causing transmission of HIV and hepatitis C, the FDA asked the manufacturer to remove Opana ER from the U.S. market in 2017. PMC+2Wikipedia+2
Evidence of Effectiveness
-
A 12-week randomized clinical trial showed Opana ER relieved chronic low back pain in patients already experienced with opioids, compared to baseline. Pain intensity and interference with function improved significantly. Oxford Academic+1
-
Labeling information and prescribing guidelines back up those findings: Opana ER produced better pain control for certain chronic moderate to severe pain when prescribed correctly. FDA Access Data+1
Conclusion: Balancing Benefits vs Risks
Opana ER can provide meaningful pain relief for certain patients with chronic severe pain, particularly when other treatments fail. However, the evidence shows the risks are substantial: abuse potential, serious adverse events (including TMA), and public health consequences have led to market withdrawal in the U.S.
If you are considering or prescribed Opana ER, you (or your healthcare provider) should weigh:
-
Can non-opioid or lower risk medications achieve sufficient pain control?
-
What risks of misuse or side effects exist in your context?
-
Are there monitoring, safety measures, and patient education in place?
For more detailed drug information, dosing guidelines, or legal/regulatory status, you might consult internal resources like The Pharmacy Meds as well as external trusted sources such as the Oxymorphone page on Wikipedia. Wikipedia





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.